- Number 301 |
- December 7, 2009
LHC pushes protons to higher energy
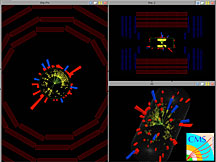
First proton-proton collisions in the
CMS detector. Credit: CMS collaboration
Accelerator operators of the Large Hadron Collider in Europe have begun the process of propelling protons to higher and higher energy. The LHC produced its first low-energy particle collisions on Nov. 23, steering two beams of protons with energy of 450 GeV into each other. Operators now have begun the process of accelerating the beams to higher energy. On Sunday evening, Nov. 29, the LHC beam energy exceeded for the first time the previous world record of 980 GeV, held by the Tevatron collider at DOE’s Fermi National Accelerator Laboratory. The start of the experimental LHC program with high-energy collisions is scheduled for the first quarter of 2010, with an energy of 3,500 GeV per beam.
Scientists from across North America are taking shifts in Fermilab’s LHC Remote Operations Center to help with the commissioning of the LHC and the recording of proton-proton collisions at the CMS experiment. More than 900 scientists from 48 institutions in the U.S. work on the CMS experiment. The Department of Energy and the National Science Foundation contributed a total of $531 million to the construction of the Large Hadron Collider and its experiments.
[Kurt Riesselmann, 630.840.5681,
kurtr@fnal.gov]
